
Ever since cars started being popular, there was a need for electricity to run all the secondary systems. Things like the headlights, rear lights, interior lights, horn, and radio, all require electricity. Most drivers take this for granted, but there is a complex system inside your car that takes care of that. Apart from the battery, the most critical part of that system is the alternator. If the engine has no alternator, it will only run until the battery drains out. The spark plugs also use electricity to run the engine if you didn’t already know. The importance of the alternator in modern cars is even more significant because it runs dozens of critical safety systems. That’s why alternator replacement can be costly, especially on some luxury cars.
But what does an alternator do, and why it is so important? We will answer that question shortly, giving you a detailed view of the electrical system in your car. Then, we will get into more detail on alternator replacement and repair and how much you can expect to pay to have your alternator replaced. Of course, we will guide you through the most common symptoms that your vehicle shows when there are alternator problems.
What is the Purpose of the Alternator?
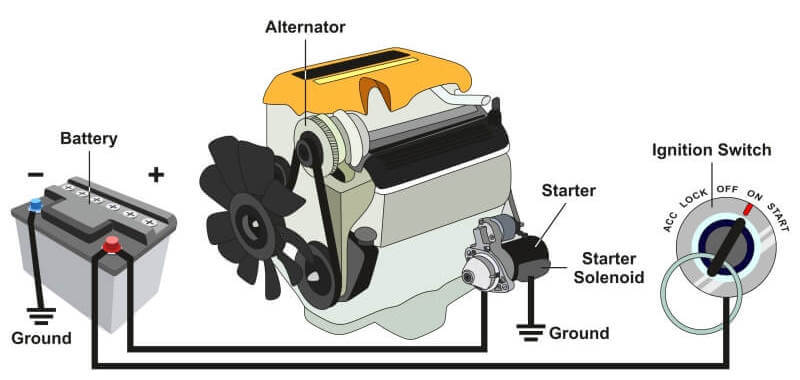
The alternator provides electricity to all systems in your car, including charging the battery. It does that by converting the kinetic energy from the engine into electric power. In other words, your engine is the one that supplies all the power, run by gasoline or diesel fuel. The alternator only converts it to electricity. For those that have generators lying around, they work on the same principle as alternators. An engine runs and produces kinetic energy, while the dynamo converts it to electricity.
Where Does the Alternator Get the Kinetic Energy From?
Every time you start your car, the alternator begins to work. That is because the crankshaft connects it directly to the engine via the serpentine belt. This belt also powers other vital systems such as the water pump and air-conditioning system. The circular movement of the crankshaft directly transfers to the alternator via the belt. The alternator then uses this kinetic energy to convert it into electric power.
In most modern cars, the alternator is situated near the front of the engine, and usually on the side. You can recognize the alternator by the vented aluminum housing, and the copper coils visible inside.
How Does it Convert Kinetic Energy to Electricity?
The alternator works like any other generator of electricity. In other words, it uses the power of electromagnetism. When it runs, it starts to generate a magnetic field, which then converts to electricity. That is opposite to an electric motor, which converts the voltage into magnetism, and then kinetic energy.
Inside, the alternator consists of a stator, rotor assembly, and diodes. The rotor is the moving part, and it turns every time you start the engine. It consists of triangular finger poles put around coil wires and an iron core that lies around the circumference. When the rotor turns, the finger poles produce a magnetic field that transfers to the stator.
The stator is the stationary part of the alternator that sits around the rotor. It captures the magnetic field and converts it to electricity. The stator has a set of three coil windings, situated at 120 degrees apart. The windings capture the strong magnetic field generated from the rotor and convert it to electricity. The reason why there are three windings is so to produce three different phases of electricity.
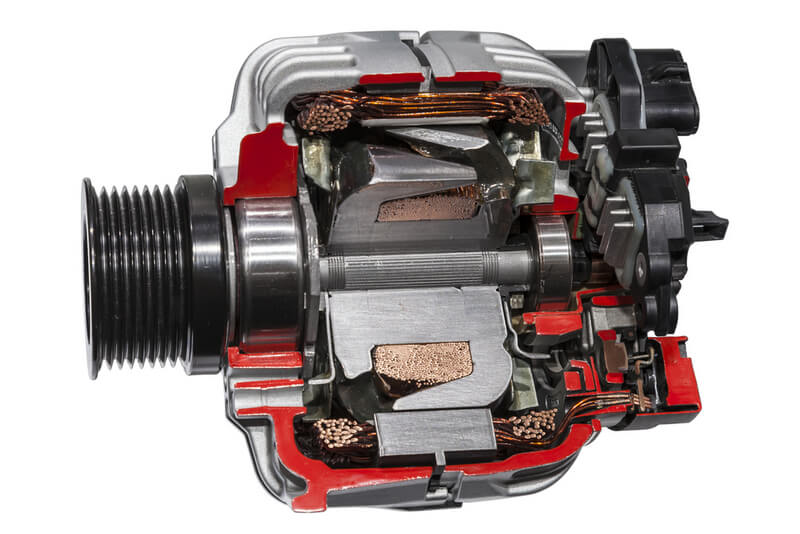

The diodes convert the generated A/C power to D/C power since most electronics work on D/C. The converted electricity then goes to the voltage regulator. This part constantly changes the voltage so that it fills the gap when the battery produces a lower voltage.
All alternators have housings made from aluminum because it is a non-magnetic metal. Aluminum is also great for cooling since alternators produce a lot of heat. The housing also has vents for even better heat dissipation. In some modern cars, there are even built-in coolers.
What Are the Symptoms of a Bad Alternator?
Numerous symptoms can point out alternator problems, but it always relates to a lack of electricity. Let’s have a look at the most common issues meaning you’ll need an alternator replacement shortly:
- The battery is dead, even though it’s new. This happens when the alternator isn’t capable of producing electricity and doesn’t charge the battery. In this case, as you drive your car, the battery will run out of power, and the engine might stall.
- Dim headlights and flickering electronics. If the alternator doesn’t supply enough power, the electric systems in your car will start to flicker. A great example of that is dim headlights, especially at lower engine RPMs. The instrument panel and the radio might begin to flash or lose power. Other systems, like the power windows or heater blower, might work slowly or not work at all.
- The battery indicator light in your car will flash. Every modern vehicle has a warning light like this. The warning light will come up as soon as the charging system gets below a set threshold.
With all that said, even if some of the symptoms arise, the alternator might not be the culprit. Sometimes, the serpentine belt might be loose. When it's the case, the alternator's pulley will start slipping and the alternator won’t get enough kinetic energy from the engine. You can always check that by pulling on the belt while the engine is not running and see if it’s tight.
How Long Does It Last?
It depends on the vehicle. Some more reliable cars might not need an alternator replacement throughout the lifecycle of the car. Others might need a replacement after 50,000 to 60,000-miles. Nonetheless, modern vehicles are very reliable in this department. On average, a modern alternator should last around 100,000-miles or over six years.
The longevity also depends on how you use the vehicle. The more electronics you use, the more the generator needs to work to pump out electricity. That is especially true if you install aftermarket accessories that drain electricity. For example, power inverters and robust Hi-Fi systems can quickly drain the alternator.
How Much Does It Cost to Get an Alternator Replacement?
It really depends on the car you own. On some economy cars with four-cylinder engines, the alternators cost around $200. However, on luxury cars with large engines and a lot of gizmos, the price of the alternators can easily go over $1000. Luckily, the labor cost is usually not that high because replacing the alternator doesn’t take a lot of time. Once again though, on some luxury cars, replacing the alternator might require the disassembly of multiple other components to be able to reach it. How accessible your alternator is will have a direct impact on the replacement cost. As a general rule, if you can easily see the alternator when opening the hood, the replacement cost shouldn't be that bad. If you can't see it because it's hidden under other components, it might be more expensive.
How Long Does It Take to Replace an Alternator?
Skilled mechanics can change it in only 30 min to an hour. However, this also depends on the type of vehicle you drive. The average alternator replacement time is around 1.5 to 2 hours.
There is a Cheaper Way
When you’re looking for an alternator replacement, you might want to check reconditioned ones. These alternators will work the same as a new one – the only difference is that they are repaired. That is usually done by the vehicle manufacturer in one of their plants. However, to get a reconditioned part, you always need to give the old part to the workshop, as a core exchange. Some mechanics can even repair your alternator, but that will take longer than just replacing it with a reconditioned one. The most affordable option is often to find an alternator repair shop near where you live. These shops will take your faulty alternator and switch it for an already rebuilt one for a fraction of the price of a new OEM one.
Alternatively, you can order a replacement alternator and change it yourself with an automotive how-to manual.
